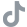-

-
About Us
- Our Vision
-
Personalized Care
Personalized Care Personalized Care Intro
Diagnostic Tests
- Digital X-Ray
- DynaROM
- 3D Body Scanning
- Gastrointentinal Health
- Organic Acids
- Comprehensive Stool Analysis
- Food Sensitivity
- Dietary Antigen Complete
- Endocrinology
- Thyroid Panel
- DUTCH Hormone Test
- Neurotransmitter Profile
- Adrenal Profile
- Nutritional Status
- Vitamin D
- Homocysteine
- Methylmalonic Acid
- Urine Iodine
- Organic Acids
- Copper Zinc Profile
- Essential Fatty Acid Profile
- RBC Metals & Minerals
- Toxic & Essential Elements
- RBC Elements
- Urine Toxic Metals
- Hair Metals & Minerals
- Urine Halides
Treatments
- Avacen Therapy
- Bioidentical Hormone Replacement Therapy (Anti-Aging)
- Chiropractic Care
- Electric Muscle & Nerve Stimulation
- Emsculpt Neo
- Emsella Treatment
- Erchonia Laser (Model EVRL)
- Exosomes
- Hair Restoration
- Headache & Migraine Treatment
- Hyaluronic Acid Injection
- Intersegmental Traction
- IV Nutrient Therapy
- Laser Lipo
- Massage Traction Chair
- PRP Facials
- PRP for Erectile Dysfunction
- PRP for Female Sexual Dysfunction
- PRP for Pain Relief
- PRP for Urinary Incontinence
- Semaglutide
- Shockwave Therapy for Cellulite & Skin Tightening
- Shockwave Therapy for Pain Relief
- Shockwave Therapy for Female Sexual Dysfunction
- Shockwave Therapy for Male Sexual Dysfunction
- Skin Rejuvenation
- Spinal Decompression
- TENS Unit
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
- Therapeutic Ultrasound
- Thyroid Care
- Trigger Point Therapy
- Durable Medical Equipment
- Ankle-foot Orthosis
- Cervical Rehab Coller
- Custom Foot Orthotics
- Lumbosacral Orthosis
- Osteoarthritis Knee Brace
- Wrist Brace
- FAQs
- Testimonials
- Pain Relief
- Weight Loss
-
Sexual Wellness
-
Anti-Aging
-
Resources
- Blog
- Video Library
- Store
-
Health Condition Library
Health Condition Library
- Ankle Osteoarthritis
- Bulging Spinal Disc
- Carpal Tunnel
- Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease
- Cervical Radiculopathy
- Elbow Bursitis
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Fatigue
- Female Hormone Imbalance
- Female Sexual Dysfunction
- Fibromyalgia
- Foot Arthritis
- Frozen Shoulder
- Golfer’s Elbow
- Hand Arthritis
- Headache
- Hip Bursitis
- Hip Osteoarthritis
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Knee Bursitis
- Knee Osteoarthritis
- Low Testosterone
- Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
- Migraines
- Musculoskeletal Pain
- Obesity
- Osteoarthritis
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Plantar Fibroma
- Rotator Cuff Injury
- Sciatica Pain
- Shoulder Bursitis
- Shoulder Osteoarthritis
- Tennis Elbow
- Thoracic Degenerative Disc Disease
- Urinary Incontinence
- Weight Gain
- Wrist Arthritis
- Wrist Bursitis
- Contact
Unveiling the Thyroid’s Role in Metabolism: How Hypothyroidism Can Tip the Scale
In the intricate symphony of our body’s functions, the thyroid gland plays a vital role as the conductor of metabolism. This small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck produces hormones that regulate various bodily processes, including energy production and weight management. However, when the thyroid falters and becomes underactive, a condition known as hypothyroidism, it can disrupt this delicate balance and lead to unwanted weight gain. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the thyroid and explore how hypothyroidism can tip the scale.
The Thyroid’s Metabolic Mastery
The thyroid gland, often referred to as the “master gland,” secretes two essential hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones act as messengers, traveling through the bloodstream to reach every cell in the body. Once inside the cells, T3 and T4 stimulate the production of proteins and regulate the rate at which cells convert oxygen and calories into energy. In other words, they are the driving force behind our metabolism.
Hypothyroidism: A Weighty Predicament
When the thyroid gland fails to produce enough T3 and T4 hormones, the body’s metabolic engine slows down. This sluggishness can manifest in various ways, with weight gain being a common symptom. As the body’s energy expenditure decreases, fewer calories are burned, and the excess energy is stored as fat. Additionally, hypothyroidism can lead to water retention and a decrease in muscle mass, further contributing to weight gain.
Unraveling the Link: Thyroid and Weight Gain
While hypothyroidism can be a contributing factor to weight gain, it is essential to understand that it is not the sole cause. Weight management is a complex interplay of various factors, including diet, exercise, genetics, and overall health. However, for individuals with an underactive thyroid, addressing the condition is crucial for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
Seeking Solutions: Treating Hypothyroidism
Fortunately, hypothyroidism can be effectively managed with the help of medical professionals. A doctor can diagnose the condition through blood tests and recommend appropriate treatment options. The most common approach involves hormone replacement therapy, where synthetic or bioidentical thyroid hormones are prescribed to supplement the body’s inadequate production. By restoring hormone levels to normal, metabolism can be reinvigorated, helping individuals shed excess weight and regain their vitality.
Conclusion:
The thyroid’s role in regulating metabolism is undeniable, and when it falters, weight gain can become an unwelcome companion. Understanding the connection between an underactive thyroid and weight gain is crucial for individuals seeking to achieve their weight loss goals. By seeking medical guidance and exploring treatment options, those affected by hypothyroidism can embark on a journey towards a healthier, more balanced life. Remember, with the right support, the scale can tip in your favor once again.