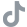-

-
About Us
- Our Vision
-
Personalized Care
Personalized Care Personalized Care Intro
Diagnostic Tests
- Digital X-Ray
- DynaROM
- 3D Body Scanning
- Gastrointentinal Health
- Organic Acids
- Comprehensive Stool Analysis
- Food Sensitivity
- Dietary Antigen Complete
- Endocrinology
- Thyroid Panel
- DUTCH Hormone Test
- Neurotransmitter Profile
- Adrenal Profile
- Nutritional Status
- Vitamin D
- Homocysteine
- Methylmalonic Acid
- Urine Iodine
- Organic Acids
- Copper Zinc Profile
- Essential Fatty Acid Profile
- RBC Metals & Minerals
- Toxic & Essential Elements
- RBC Elements
- Urine Toxic Metals
- Hair Metals & Minerals
- Urine Halides
Treatments
- Avacen Therapy
- Bioidentical Hormone Replacement Therapy (Anti-Aging)
- Chiropractic Care
- Electric Muscle & Nerve Stimulation
- Emsculpt Neo
- Emsella Treatment
- Erchonia Laser (Model EVRL)
- Exosomes
- Hair Restoration
- Headache & Migraine Treatment
- Hyaluronic Acid Injection
- Intersegmental Traction
- IV Nutrient Therapy
- Laser Lipo
- Massage Traction Chair
- PRP Facials
- PRP for Erectile Dysfunction
- PRP for Female Sexual Dysfunction
- PRP for Pain Relief
- PRP for Urinary Incontinence
- Semaglutide
- Shockwave Therapy for Cellulite & Skin Tightening
- Shockwave Therapy for Pain Relief
- Shockwave Therapy for Female Sexual Dysfunction
- Shockwave Therapy for Male Sexual Dysfunction
- Skin Rejuvenation
- Spinal Decompression
- TENS Unit
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
- Therapeutic Ultrasound
- Thyroid Care
- Trigger Point Therapy
- Durable Medical Equipment
- Ankle-foot Orthosis
- Cervical Rehab Coller
- Custom Foot Orthotics
- Lumbosacral Orthosis
- Osteoarthritis Knee Brace
- Wrist Brace
- FAQs
- Testimonials
- Pain Relief
- Weight Loss
-
Sexual Wellness
-
Anti-Aging
-
Resources
- Blog
- Video Library
- Store
-
Health Condition Library
Health Condition Library
- Ankle Osteoarthritis
- Bulging Spinal Disc
- Carpal Tunnel
- Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease
- Cervical Radiculopathy
- Elbow Bursitis
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Fatigue
- Female Hormone Imbalance
- Female Sexual Dysfunction
- Fibromyalgia
- Foot Arthritis
- Frozen Shoulder
- Golfer’s Elbow
- Hand Arthritis
- Headache
- Hip Bursitis
- Hip Osteoarthritis
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Knee Bursitis
- Knee Osteoarthritis
- Low Testosterone
- Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
- Migraines
- Musculoskeletal Pain
- Obesity
- Osteoarthritis
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Plantar Fibroma
- Rotator Cuff Injury
- Sciatica Pain
- Shoulder Bursitis
- Shoulder Osteoarthritis
- Tennis Elbow
- Thoracic Degenerative Disc Disease
- Urinary Incontinence
- Weight Gain
- Wrist Arthritis
- Wrist Bursitis
- Contact
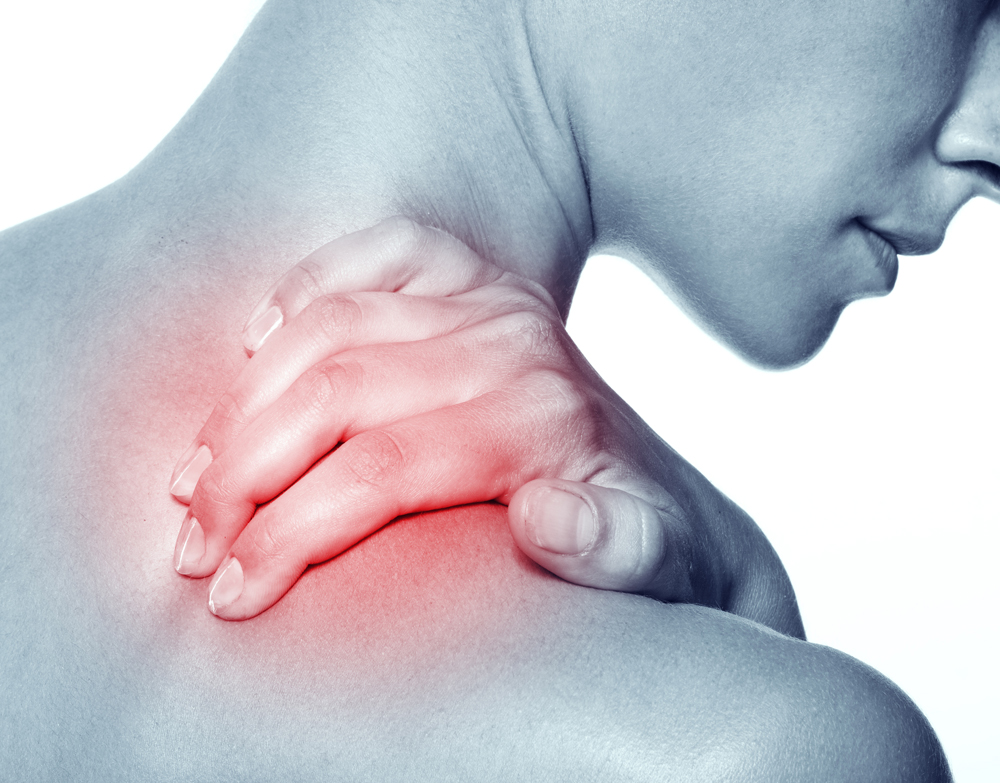
Understanding Musculoskeletal Pain
Alternate Names: Musculoskeletal pain is also known by other names such as musculoskeletal discomfort, musculoskeletal disorder, musculoskeletal syndrome, or simply as pain in the muscles and bones.
Introduction:
Musculoskeletal pain, also known as musculoskeletal discomfort, refers to pain or discomfort that affects the muscles, bones, ligaments, tendons or other structures supporting the body’s movement. It is a common condition that can have various causes and can occur in different parts of the body. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what musculoskeletal pain is, its alternate names, common symptoms, underlying causes, and multiple treatment options available.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of musculoskeletal pain can vary depending on the underlying cause and the specific area of the body affected. Common symptoms include:
- Pain or discomfort in the muscles, bones, joints, or surrounding tissues.
- Stiffness or limited range of motion in the affected area.
- Swelling or inflammation in and/or around the affected area.
- Muscle weakness or fatigue.
- Tenderness or sensitivity to touch.
- Difficulty sleeping due to pain.
Causes:
Musculoskeletal pain can have various causes, including:
- Muscle strains or sprains: Overexertion, sudden movements, or improper lifting techniques can lead to muscle strains or sprains, causing localized pain.
- Injuries: Traumatic injuries, such as fractures, dislocations, or ligament tears, can result in musculoskeletal pain.
- Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or gout can cause chronic musculoskeletal pain.
- Fibromyalgia: This is a chronic disorder described by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness.
- Poor posture: Maintaining incorrect posture for extended periods can lead to muscle imbalances and pain.
- Repetitive strain injuries: Overuse of certain muscles or repetitive movements can cause musculoskeletal pain, such as carpal tunnel syndrome or tennis elbow.
- Infections or inflammations: Conditions like bursitis, tendinitis, or cellulitis can cause localized musculoskeletal pain.
- Nerve compression: Conditions like herniated discs or pinched nerves can result in radiating musculoskeletal pain.
Multiple Treatment Options:
The treatment options for musculoskeletal pain depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here are some common treatment approaches:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help alleviate mild to moderate musculoskeletal pain. Although NSAIDs do reduce inflammation to temporarily relieve pain, they are responsible for 30% of hospital admissions for adverse drug side effects, mainly due to bleeding, heart attack, stroke, and kidney damage. In addition, from the first day of use, all NSAIDs increase the risk of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding, myocardial infarction, and stroke.
- Physical therapy: Targeted exercises, stretches, and manual therapy techniques can help improve muscle strength, flexibility, and reduce pain.
- Heat or cold therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Rest and activity modification: Resting the affected area and avoiding activities that worsen the pain can promote healing.
- Assistive devices: The use of braces, splints, or orthotic devices can provide support and relieve stress on the affected area.
- Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and incorporating regular exercise can help prevent and manage musculoskeletal pain.
- Alternative therapies: Techniques such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, massage therapy, or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) may provide relief for some individuals.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation and relieve pain in certain conditions. Side effects of cortisone, which is commonly injected for joint pain, includes thinning of the skin, easy bruising, weight gain, puffiness of the face, elevation of blood pressure, cataract formation, thinning of the bones, and a rare but serious form of damage to large joints (avascular necrosis). Due to risks, patients may only get this treatment once every several months.
- Surgical intervention: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical procedures may be considered to address the underlying cause of musculoskeletal pain.
Conclusion:
Musculoskeletal pain is a common condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. By understanding what musculoskeletal pain are, its alternate names, common symptoms, underlying causes, and multiple treatment options available, individuals can make informed decisions about managing and seeking appropriate care for their musculoskeletal pain. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for a precise diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.